variable head permeability test discussion|falling head vs constant permeability : trader Figure 12.7 Variable head tests in boreholes, (a) Falling head test. Water is added to the borehole to raise water levels, inducing flow from the borehole into the surrounding strata, (b) Rising head test. 10 de jul. de 2023 · Martina é nova no ramo: há cerca de oito meses, foi assaltada, teve seu celular roubado e, para conseguir outro, decidiu seguir o caminho do "conteúdo adulto". .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Agende já seu Eletroneuromiografia Agende já o seu exame de Eletroneuromiografia na Mega Imagem! A Eletroneuromiografia é um .
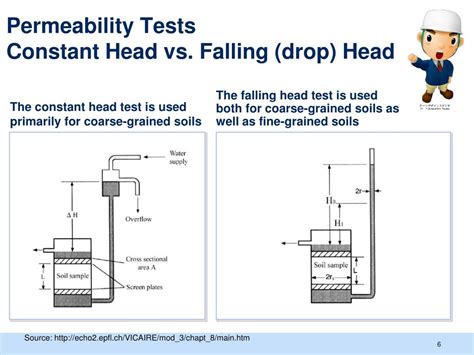
Variable head permeability test is one of several techniques by which the permeability of soil is determined. It is used to evaluate the permeability of fairly less previous soil. Permeability is the measure of the ability of soil to allow .Figure 12.7 Variable head tests in boreholes, (a) Falling head test. Water is added to the borehole to raise water levels, inducing flow from the borehole into the surrounding strata, (b) Rising head test.In the laboratory we employ two methods. One is constant head permeability test. And another one is Falling head or variable head permeability test. These tests measure the amount of water that goes through a soil sample in a fixed .
This test helps measure the permeability of soil, especially for less compacted types. The permeability impacts various aspects, such as settlement rates under loads, the design of . CONSTANT HEAD PERMEABILITY TEST. Primarily used for coarse-grained soils. A constant head of water is applied to each end of soil in a “permeameter”. After a .Constant Head Test refers to an apparatus where the same relative elevation of the top of the water column (head pressure) remains over the sample throughout the test. It is a valid test for soils with a high rate of flow like sands and .Appendix 2: Execution and Analysis of Variable Head Permeability Tests in Boreholes. A2.I GENERAL COMMENTS ON PERFORMING PERMEABILITY TESTS. Many factors may influence the results obtained from in situ .
Variable-head permeability tests are often conducted in the field to determine local hydraulic conductivity values for soils. Many methods were developed over the years to interpret.
falling head vs constant permeability
Variable-head permeability tests can be performed in open boreholes or monitoring wells having either a long screen or several screened zones. In all cases, a test . Variable-head permeability tests are often conducted in the field to determine local hydraulic conductivity values for soils. Many methods were developed over the years to interpret such tests.During a variable-head permeability test, the flux Q (m3/s) in the soil is equal to the flux Q inj (m3/s) in the injection pipe. The flux in the soil depends upon the shape factor of . Abstract. Two types of variable-head permeability tests in driven flush-joint casings, the end-of-casing test and the lateral injection test (Lefranc test), were performed in two sand tanks. Hydraulic conditions in the sand tanks included a constant vertical hydraulic gradient that was null, positive, or negative. The gradients were monitored by lateral piezometers, .
This method, also called the Variable Head Permeability test, is suitable for fine grain soils with intermediate-low permeability such as clays and silts. . This test refers to the Constant head permeability method. At the time of writing, VJ Tech complies to BS1377-6:1990, EN ISO 17892-11 and D5484-16 (Method A). a. Sample Preparation.
falling head tests in borehole
Soil Lab Boss Dave Anderson demonstrates how a falling head permeability test is performed using a triaxial shear testing apparatus. This video explains the procedure of constant head test to determine the soil permeability. This test is performed on coarse-grained soil with a high coeffic.
The document describes procedures for conducting a falling head permeability test to determine the coefficient of permeability (k) of soils. The test involves measuring the change in water height over time as water flows through a soil sample confined in a standpipe. The k value is then calculated using an equation that relates the height changes, sample dimensions, and elapsed .
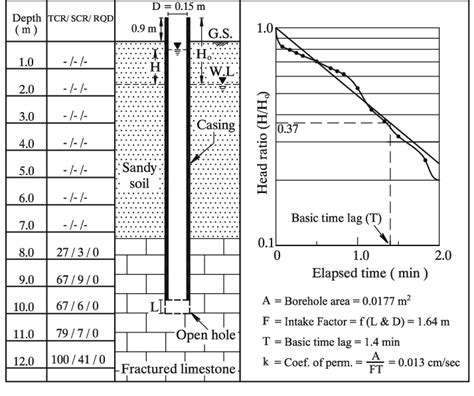
Fig. 6 shows the variation of the coefficient of permeability with depth estimated from the CPT soundings compared to the falling head test results. The values of the coefficient of permeability measured from the falling head permeability test varied between 4.21 × 10 −5 m/s and 4.11 × 10 −4 m/s, with an average value of 2.43 × 10 −4 m/s 3. Supplies and materials for Falling Head Method: 1-Perneameter device. 2- Standpipe with ring stand and clamp. 3- Distilled water. 4-Timer. 5- Thermometer. 6- Graduated cylinder. 7- Ruler (scale). Test Procedure Constant Head Test : 1) Remove a loading piston of permeameter cell, then measure the inside diameter, height of it and the distance between .
Situation 1 For a variable head permeability test, the following data were given: Length of specimen= 37.5 cm; Area of specimen= 19.4 sq.cm; Coefficient of permeability= 0.002912 cm/sec. 2 points What should be the area of the standpipe for the head to drop from 63.5 cm to 30.5 cm in 8 minutes?Permeability of a coarse grained soil can be determined by a constant head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.1-2001; ASTM D2434), and in a fine grained soil, falling head permeability test (AS1289.6.7.2-2001; ASTM D5856) works the best. The Constant head permeability test follows the principle of Darcy’s Law [29] and therefore, it is recommended by the ACI [9]. In that regard, the test measures the amount of water that goes through a sample in a determined time.
moisture meter kmart
Non-steady flow in the variable-head permeability test Open PDF. Géotechnique. ISSN 0016-8505 | E-ISSN 1751-7656. Volume 55 Issue 9, November 2005, pp. 703-703. Prev Next > Non-steady flow in the variable-head permeability test . There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory: The constant head test method, and (2) the falling head test method. The constant head test method is used for permeable soils (k>10-4 cm/s) and; The falling head test is mainly used for less permeable soils (k<10-4 cm/s). Standard Reference:
Abstract. Variable-head permeability tests can be performed in open boreholes or monitoring wells having either a long screen or several screened zones. In all cases, a test involves several layers composed of fractured rocks or pervious soils. In the hole or the pipe, the static water level represents some mean value of the hydraulic heads within the aquifer layers, .There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory: (1) the constant head test method, and (2) the falling head test method. The constant head test method is used for permeable soils (k>10-4 cm/s) and the falling head test is mainly used for less permeable soils (k<10-4 cm/s). The constant head permeability test is a standard laboratory testing method for determining the permeability of granular soils containing little or no silt o.
D 4254 Test Methods for Minimum Index Density of Soils and Calculation of Relative Density3 3. Fundamental Test Conditions 3.1 The following ideal test conditions are prerequisites for the laminar flow of water through granular soils under constant-head conditions: 3.1.1 Continuity of flow with no soil volume change during a test, Variable Head Permeability Tests in Monitoring Wells: Comparing the Shape Factor Defined by Bouwer and Rice (1976) to the Shape Factor Given by Hvorslev (1951).” . Recovery Test after a Constant-Head Test in a Monitoring Well: Interpretation Methods and .Here is a comparison of the constant head and falling head permeability. The constant head test is used to determine the coefficient of permeability (k) of soil by applying a constant water charge to sample, measuring the quantity of water flowing through the specimen over time. . Soil Parameters Affecting Accurate Permeability Testing . This test method is used to determine the coefficient of permeability (K) having units of velocity or m/sec. Designation of the test; This test method has been standardized by American Association for State Highway and Transportation Officials under AASHTO – T – 215.
moisture meter kennards
discussion. 3 CONSTANT HEAD PERMEABILITY TEST (ASTM D2434) . FALLING/VARIABLE HEAD PERMEABILITY TEST (ASTM D5084) • Mainly used for fine-grained soils but can . In a falling head permeability test, a soil sample of 7585mm2 cross-section and 210.2mm length was subjected to a flow ofThe falling head method of determining permeability is used for soil with low discharge, whereas the constant head permeability test is used for coarse-grained soils with a reasonable discharge in a given time. For very fine-grained soil, capillarity permeability test is recommended. Usually, permeability of soils is determined by two methods: 1. 2. For such soils, the variable head permeability test in used. This test is recommended for soils with coefficient of permeability in the range 10-3 to 10-7 cm/s and maximum particle size of 9.5 mm. Typical values of permeability (k) Sr. No. Soil type coefficient of permeability (mm/ sec) Drainage property 1 Clean Gravel 10+1 to 10+2 Very Good 2 .It also called variable-head test. For relatively less permeable soils, the quantity of water collected in the graduated cylinder of the constant-head permeability test is very small and cannot be measured accurately. For such soils, the falling head permeability test is . DISCUSSION 1- What is the effect of the degree of saturation on the .
PART I. CONSTANT-HEAD PERMEABILITY TEST METHOD A. SCOPE. The permeability test is a measure of the rate of the flow of water through soil. In this test, water is forced by a known constant pressure through a soil specimen of known dimensions and the rate of flow is determined. This test is used primarily to. determine the suitability of sands .Discover the process of conducting a falling head permeability test for soil mechanics on YouTube.
falling head soil permeability apparatus
24 de ago. de 2020 · Wait 5 seconds and click on the blue ‘download now’ button. Now let the download begin and wait for it to finish. Once Five Nights At Freddy’s is done downloading, right-click the .zip file and click on .
variable head permeability test discussion|falling head vs constant permeability